eduGMAT® mini-test 1: Arithmetic Exercises
| Numbers Numbers are classified according to their type. The first type is the one you have known since elementary school: Natural numbers (whole positive numbers) – are the numbers used for counting: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, … Adding 0 and the negatives of the naturals, we obtain Integers – numbers from the set {…, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, … } Note: The integer 0 is neither positive nor negative. 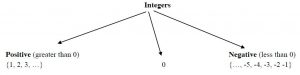 |
[qsm quiz=15]
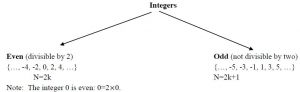
Properties of even/odd integers |
[qsm quiz=16]
| The numbers –2, –1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 are consecutive integers. Consecutive integers can be represented by n, n + 1, n + 2, n + 3, . . . , where n is an integer. The numbers 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 are consecutive even integers. Consecutive even integers can be represented by 2n, 2n + 2, 2n + 4, . . . , where n is an integer. The numbers 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 are consecutive odd integers. Consecutive odd integers can be represented by 2n + 1, 2n + 3, 2n + 5, . . . , where n is an integer. Note: if the numbers are given in the problem in a raw like a, b, c it does not mean that a<b<c. Properties:
|
[qsm quiz=17]
| A prime number is a positive integer that has exactly two different positive divisors: 1 and itself. For example, 2, 3, 5 are prime numbers, but 15 is not, since 15 has four different positive divisors, 1, 3, 5, and 15. First prime numbers are: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47… Note: If the number less than 100 is not divisible by 2, 3, 5, 7, it is prime. Note: The number 1 is not a prime number since it has only one positive divisor. Note: 2 is the only even prime. Indeed, if a prime greater than 2 were even, it would have at least three different divisors: 1, itself and 2. |
[qsm quiz=18]

